Getting Started
Get Agor running and create your first AI coding session in under 5 minutes.
Installation
npm install -g agor-liveQuick Start
# 1. Initialize (creates ~/.agor/ and database)
agor init
# 2. Start the daemon
agor daemon start
# 3. Open the UI
agor openThat’s it! Now follow the steps below to start your first AI coding session.
Try in GitHub Codespaces (up in 1-2 minutes):
Step 1: Link a Code Repository
Before you can create AI sessions, Agor needs to know about your code repositories.
Add a Local Repository
If you have a git repository on your machine:
Via UI:
- Open Agor (
agor open) - Click Settings (⚙️ icon in header)
- Go to Repos tab
- Click Add Repository
- Enter the absolute path to your repo (e.g.,
/Users/you/projects/myapp)
Via CLI:
agor repo add /path/to/your/repoAdd a Remote Repository
Agor can clone remote repositories for you:
Via UI:
- Open Settings → Repos
- Click Add Repository
- Enter the git URL (e.g.,
https://github.com/username/repo.git) - Agor will clone it to
~/.agor/repos/<repo-name>

Via CLI:
agor repo add https://github.com/username/repo.gitStep 2: Create Your First Worktree
What’s a worktree? A worktree is an isolated working directory for your repository - think of it as checking out a branch in a separate location. This lets you work on multiple features simultaneously without switching branches or stashing changes.
Why Worktrees?
Git worktrees allow you to have multiple branches checked out at once in different places on your filesystem. In Agor:
- 1 worktree = 1 issue = 1 PR = 1 feature
- Each worktree contains a tree of AI sessions working on that feature
- Completely isolated - changes in one don’t affect others
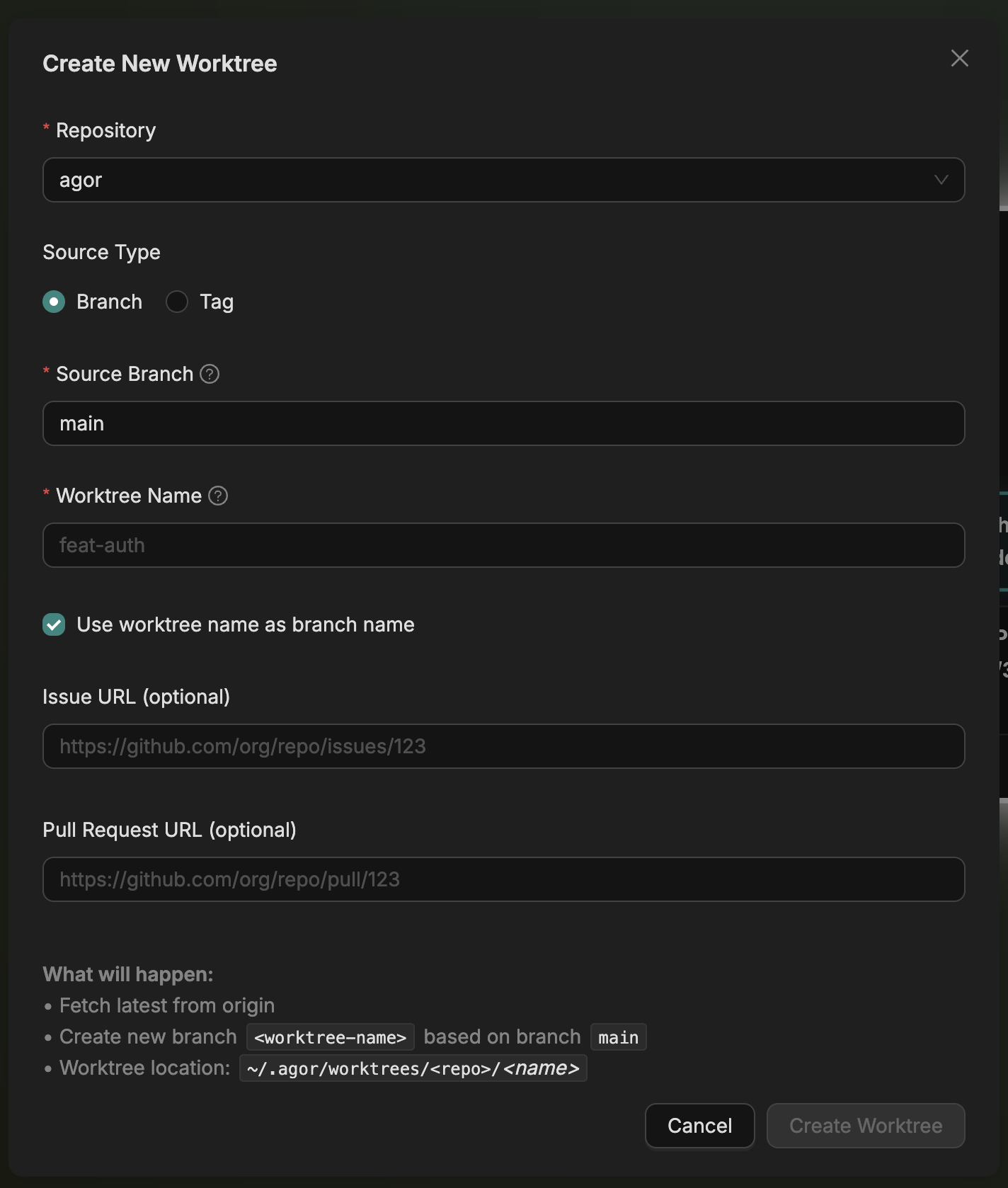
Create a Worktree
Via UI:
- Click New Worktree button (+ icon near top)
- Choose your repository
- Pick a name (like you would for a branch - e.g.,
auth-feature,fix-bug-123) - Optionally:
- Create a new branch or checkout existing one
- Link to an issue URL or PR URL
- Add notes about what you’re working on
Via CLI:
# Create worktree with new branch
agor worktree create my-repo feature-name
# Create from existing branch
agor worktree create my-repo feature-name --branch existing-branch
# Link to issue
agor worktree create my-repo feature-name --issue https://github.com/user/repo/issues/123Your worktree will be created at ~/.agor/worktrees/<repo>/<name>
Step 3: Authenticate with AI Providers
Agor supports multiple AI coding agents (Claude Code, Codex, Gemini, OpenCode). To use them, you need to authenticate.
Authentication Options
Agor offers three ways to configure AI credentials, in order of priority:
Option 1: CLI Login (Recommended for Claude)
The fastest way to get started with Claude Code:
claude loginThis stores your credentials in ~/.claude/ and Agor automatically detects them.
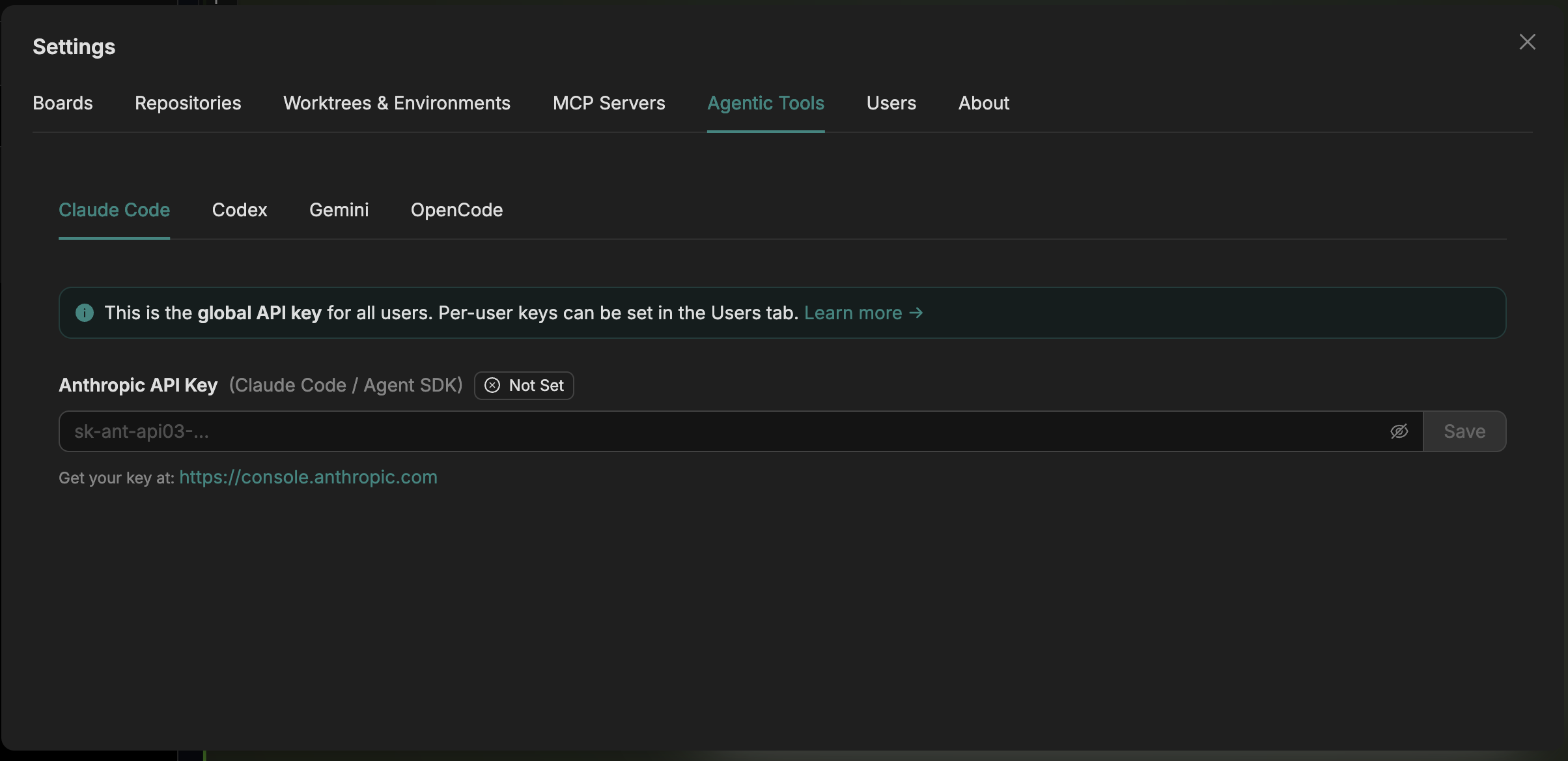
Option 2: Per-User API Keys (Recommended for Teams)
Store encrypted API keys in Agor, scoped to your user account:
Via UI:
- Open Settings → Agentic Tools tab
- Enter your API keys:
- Anthropic API Key for Claude Code
- OpenAI API Key for Codex
- Google AI API Key for Gemini
- Click Save
Your keys are:
- ✅ Encrypted at rest in the database
- ✅ Only visible to you (per-user scope)
- ✅ Automatically used by all your sessions
Get API Keys:
- Anthropic: https://console.anthropic.com/settings/keys
- OpenAI: https://platform.openai.com/api-keys
- Google AI: https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey
Option 3: Environment Variables (Global Fallback)
Set environment variables that all users can access (workspace-level):
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-ant-..."
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..."
export GOOGLE_AI_API_KEY="..."Via UI (Global Settings):
- Open Settings → Environment Variables tab
- Add variables for your workspace
Note: Environment variables are visible to all users in your Agor instance.
How Authentication Priority Works
When you start a session, Agor checks for credentials in this order:
- Per-user API keys (if set in Settings → Agentic Tools)
claude logincredentials (if you ranclaude login)- Environment variables (global fallback)
This lets you mix approaches - use claude login for yourself while teammates use per-user keys.
Step 4: Start Your First AI Session
Now you’re ready to create an AI coding session!
Via UI:
- Find your worktree card on the board
- Click New Session (+ icon on the worktree card)
- Choose your agentic tool (Claude Code, Codex, or Gemini)
- Optionally configure:
- Model selection
- Permission mode (auto-approve tools, ask before each, etc.)
- MCP servers
- Click Create
Via CLI:
# Create session in your worktree
agor session create <worktree-id> --tool claude-code
# Or use interactive mode
agor session create <worktree-id> --interactiveSend Your First Prompt
Once the session is created:
- Click on the session to open the conversation view
- Type your prompt (e.g., “Add a login form to the app”)
- Hit Enter or click Send
Watch as the AI agent:
- Reads your code
- Plans changes
- Edits files
- Runs tests
- Reports back to you
All tool calls, file edits, and command outputs are streamed in real-time!
What’s Next?
Now that you have your first session running:
- Concepts - Deep dive into worktrees, boards, sessions, and environments
- Advanced Features - Zones, subsessions, schedulers, and more
- Architecture - System design and internals
- Development Guide - Contributing to Agor
Pro Tips:
- Use zones on your board to automate workflows (drag worktree to “Ready for Review” → auto-prompt for code review)
- Fork sessions to try different approaches to the same problem
- Spawn subsessions to delegate subtasks to child agents
- Check the environment status to see if your dev server is running
Troubleshooting
Port 3030 already in use
# Find and kill the process
lsof -ti:3030 | xargs kill -9
# Or configure a different port
agor config set daemon.port 4030
agor daemon startDaemon not starting
# Check daemon status
agor daemon status
# View logs
agor daemon logs
# Check health endpoint
curl http://localhost:3030/healthCan’t connect to daemon
Make sure the daemon is running:
agor daemon status
# If not running:
agor daemon startGetting Help
- Discord - Join our Discord community for support and discussion
- GitHub Discussions - Ask questions, share ideas
- GitHub Issues - Report bugs, request features
Next Steps
- Concepts - Learn about worktrees, boards, sessions, and environments
- Run
agor --helpfor complete CLI documentation - Development Guide - Contributing to Agor
- Architecture - System design and internals